One of the most important aircraft documents is the Airworthiness Certificate. The certification by the FAA that the aircraft meets the required safety standards to be deemed.Airworthy and that it is therefore permitted to operate in the airspace of the United States.
Owners of small aircraft and airlines that own and operate commercial aircraft fleets are required to possess Airworthiness Certificates. Aircraft for which Airworthiness Certificates are not obtained do not conform to aviation regulation and the owners and operators are subject to regulatory action and fines, and lives are endangered. This guide covers the types of Certificates, their uses, renewals, and compliance within.
What Is an Airworthiness Certificate and Why It Matters
An Airworthiness Certificate is a document that validates that an aircraft is in a condition for safe operation after inspection by the person authorized under 14 CFR part 21. It is illegal to fly without this certificate, regardless of the aircraft’s condition or who owns it.
Key Types of Airworthiness Certificates
Type Purpose Common Use
Commercial airlines, private aircraft, cargo planes, and so on all comply with all FAA safety and performance standards.
For aircraft that cannot be certified under standard criteria. Experimental, restricted, or light-sport aircraft.
Importance of the Airworthiness Certificate
- Legal Operation: Required by law for flight in U.S. airspace.
- Safety Assurance: Assesses for compliance with manufacturer and FAA safety standards.
- Insurance Compliance: Verify compliance for aviation insurance policies.
- Resale Value: Increases buyer confidence in aircraft marketability.
An aircraft’s Airworthiness Certificate is a statement of discipline in maintenance, regulatory compliance, and operational integrity.
The Process of Obtaining an Airworthiness Certificate
For obtaining an Airworthiness Certificate, including in it the associated documentation, inspections and certification, the FAA ensures that the aircraft meets standards of structural soundness, airworthiness and maintenance.
Eligibility Determination
Before application, the aircraft must:
- Be registered with the FAA.
- Comply with its type certificate specification.
Have all required inspections performed by a certified mechanic or repair station.
Submit FAA Form 8130-6
Application for the Airworthiness Certificate is made by submitting FAA Form 8130-6 which includes identification, ownership, and maintenance information.
| Document | Required Purpose | Description / Importance |
| Aircraft Registration Certificate | Confirms ownership | Official proof linking the aircraft to its registered owner |
| Maintenance Logbooks | Verifies airworthiness maintenance | Records all inspections, repairs, and maintenance activities |
| Type Certificate Data Sheet | Confirms aircraft design compliance | Ensures the aircraft meets manufacturer and aviation authority standards |
| Weight and Balance Records | Ensures operational stability | Maintains safety by confirming proper weight distribution for flight |
FAA or DAR Inspection
An FAA ASI or DAR inspects the aircraft to ensure regulatory compliance. They review:
- Aircraft structure and systems
- Avionics functionality
- Required placards and markings
- Logbook entries and maintenance status
Issuance of Certificate
Once an airplane model has been certified, the FAA issues an Airworthiness Certificate to be displayed near the pilot’s station.
Continuous Compliance
The certificate remains valid as long as the aircraft is in compliance with the questioned FAA regulations.
Understanding Standard vs. Special Airworthiness Certificates
The FAA classifies two broad types of Airworthiness Certificates, depending on the intended design, purpose, and regulation of the aircraft.
Standard Airworthiness Certificate
This applies to the aircraft built to specifications.
- Common Categories
- Transport
- Normal
- Utility
- Acrobatic
- Commuter
Special Airworthiness Certificate
Issued for aircraft that do not meet the normal requirements, but may be flown under certain conditions.
- Experimental: For testing of new aircraft or technology.
- Restricted: Used for agricultural or aerial survey operations.
- Provisional: Used upon aircraft awaiting certification.
- Light-Sport Aircraft (LSA): Approval is simpler for recreation.
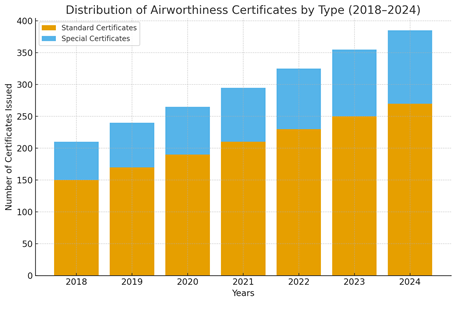
The numbers reflect a substantial increase in the standard certifications due to stricter safety regulations and to a growing general aviation fleet.
Compliance, Renewal, and Validity Requirements
An Airworthiness Certificate remains effective if the aircraft meets the conditions for issue. Authorities can suspend or revoke it.
Key Maintenance Requirements
- Annual Inspection: An approved mechanic must do it within every 12 months (one year period).
- 100-Hour Inspection: Someone must inspect after each 100 hours of flight time for an aircraft when people rent or use it.
- Airworthiness Directives (ADs): Comply with these without exception right upon receipt from the manufacturer or FAA.
Renewal Process
For Renewal, Airworthiness Certificates are not like registering because they do not expire, but they must comply continuously to remain valid.
Preventive maintenance keeps an aircraft in legal operating condition. A FAA-certificated mechanic must inspect the aircraft every 12 months to confirm its airworthiness and maintain its certification. During an AD compliance check, maintenance personnel verify that they have completed all required actions specified in the FAA Airworthiness Directive. The aircraft owner/operator records such entries in the logbook after each service event.
Revocation Triggers
- Failing to comply with safety orders.
- Unauthorized modifications.
- Use beyond approved operating limitations.
Maintaining Airworthiness Certificate in a Private Fleet
The corporate aviation department had five business jets. Following the report of minor systems irregularities with one aircraft, the FAA conducted an inspection. Logbook records, maintenance records, and inspection schedules show that all five aircraft met FAA Airworthiness Certificate requirements.
Outcome:
- Avoided operational downtime.
- Improved fleet reliability and insurance rates.
- Demonstrated compliance readiness during FAA audits.
It thus stands for the proposition that if you comply preemptively, you may certify perpetually.
Practical Tips for Managing Airworthiness Certificate Compliance
- Logbooks should record all inspections: repairs, and modifications to keep documentation updated.
- Know ADs: The FAA issues Airworthiness Directives (ADs) in periodicals that can appear at regular intervals.
- Qualified Maintenance Providers: Inspection and repair should be performed, whenever possible, at certified repair shops.
- Display the Certificate Properly: It must be displayed at all times inside of the aircraft cabin.
Tip Purpose
- Maintain organized logs: Easier FAA verification
- Track AD Implementation: Avoids penalties
- Schedule Inspections Early: Prevents grounding delays
- Audit internally for improved confidence regarding compliance.
Comparing Airworthiness Certificate and Registration Certificate
While both documents are essential, they serve distinct purposes.
| Feature | Airworthiness Certificate | Aircraft Registration Certificate |
| Purpose | Confirms aircraft safety compliance | Establishes legal ownership |
| Issuing Authority | FAA | FAA |
| Validity | Continuous, if compliant | 3 years |
| Renewal | No expiration (conditional) | Every 3 years |
| Display Location | Pilot’s cabin | Accessible within aircraft |
Together, these certifications form the foundation of legal and safe aircraft operation in the United States.
Ensuring Continuous Airworthiness Certificate
At National Aviation Center, obtaining and maintaining an Airworthiness Certificate is not just a legal requirement, it is the basis of flight safety. This means your aircraft meets FAA specifications and requirements, the specifications of the aircraft manufacturer and is in the best possible condition to operate safely and effectively.
Whether you are an individual owner, fleet operator or aviation maintenance manager, Airworthiness protects your investment, ensures compliance with regulations and helps impart passenger confidence.




