The Federal Aviation Administration is primarily responsible for ensuring aviation safety, compliance, and accurate records of aircraft in the United States. One of its key administration tasks involves renewal processes so that the registration details of an aircraft is current is legal. Aircraft owners, operators, and aviation professionals must understand how renewal works and its consequences to avoid penalties, grounding issues or delays in regulation.
The renewal requirements aim to ensure the National Aircraft Registry remains accurate and trustworthy. On a periodic basis, they approve ownership and address changes and operational status. Although it may seem mundane, failing to fulfil renewal obligations can lead to serious complications like registration lapse and loss of operating authority.
The process for renewing an FAA authorization follows certain rules and timelines. The main focus is accuracy and accountability to avoid interruption of registration status; the owners are required to furnish the information in specified periods.
This guide details the renewal process. This includes its aim, principal requirements, comparisons, practical steps, and tips for the conformity. Awareness of the Federal Aviation Administration processes for renewal might help aviation stakeholders in smooth operations and a long-term regulatory assurance.
A closer look at FAA Reauthorization
The Federal Aviation Administration’s renewal framework ensures accuracy and legality of data on registration of aircraft. Renewal is not merely a formality. It ensures that a company’s operations are legal and legitimate.
Aircraft registrations do not last forever. A license is valid for limited time; however, it has to be renewed. Registry authorities may remove inactive aircraft from the registry and update ownership records.
The main focus of the renewal framework is three primary goals. Initially it examines ownership data. Secondly, it certifies that the aircraft remains eligible for registration. A third proactive step involves updating administrative records with most recent contact details and addresses.
| Component | Purpose | Regulatory Impact |
| Ownership Verification | Confirms legal control | Prevents registry errors |
| Status Confirmation | Validates active aircraft | Improves safety oversight |
| Record Updates | Maintains accurate data | Supports enforcement |
| Renewal Cycle | Enforces compliance timeline | Ensures consistency |
Compliance Factors and Requirements for Renewal
To maintain authorization, the Federal Aviation Administration requires the renewal of FAA mandates by certain times. Although standardized, these requirements must be carefully followed.
Principal Recharging Components
For aircraft renewal, reconciling the aircraft with its owner/s is vital. To avoid a rejection and delay, information must match record.
Please submit on time. Regularly requested, renewals take place over fixed periods. Failing to meet deadlines may lead to lost registration, which inhibits legal functioning.
Documentation accuracy is also important. Processing delays or administrative follow-up can result from inconsistent or incomplete information.
Significance of Renewal Process
Renewal reestablishes accountability. This ensures aircraft owners positively affirm the registration status and not rely on old records.
It also aids in safety monitoring Accurate registration information allows regulators to contact owners about safety notices or compliance matters.
Factors for Key Renewal Compliance
- Correct airplane ID.
- Recent owner details
- On-time submission within renewal window.
- Regular private data.
Frequent Problems That Stalls Renewals
- Old addresses.
- Who owns what?
- Unsatisfied forms.
- not on time.
Renewal is often confused with other registry actions. Each possesses a distinct administrative objective and exerts a different regulatory effect.
In comparison, the FAA Registry Actions
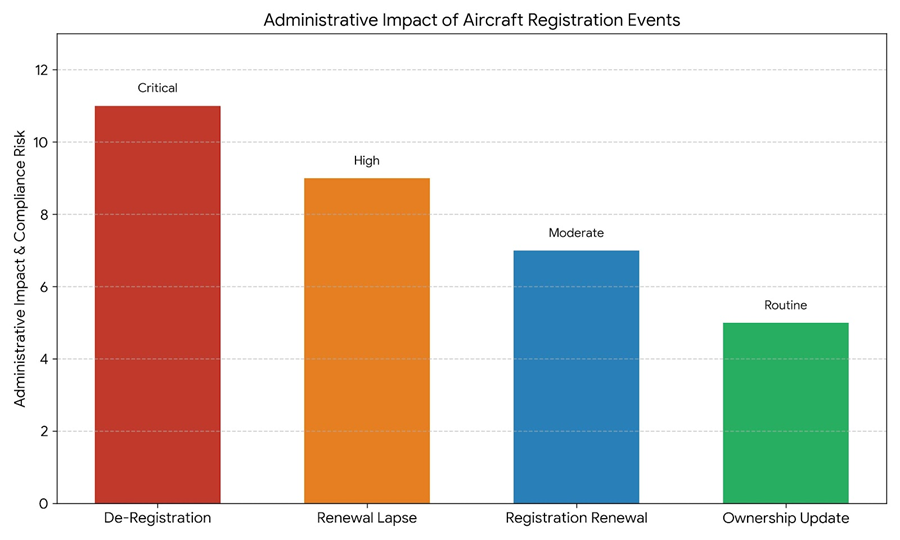
- The highest bureaucracy impact is on Critical Operational Loss which is the situation of De-Registration. Here aircraft is removed from the registry permanently. This means that the aircraft cannot operate legally until the proper application is made again to the authorities for re-registration.
- Validity and Enforcement: The event of a Renewal Lapse is classified as high risk. This means that while the aircraft remains on the registry instrument, the legal validity of the registration lapses. As a result, the aircraft must be immediately grounded and can be subject to enforcement action by the relevant aviation authorities.
- Essential Maintenance: A Registration Renewal is regarded as a moderate-impact yet essential action. This action helps sustain continuous operations in a legally-compliant manner. Moreover, it combats the Increasing Compliance Risk from a lapsed registration.
A comprehensive guide for the renewal process
To complete renewal correctly requires a process. Following steps clearly helps avoid mistakes and delays.

Steps Before Renewal
Preparation commences with a review of present registry information. Aircraft owner should check name, address and aircraft identifiers are correct.
Getting things ready early gives you time to fix up any discrepancies before you submit. The chances of the administrative rejection decrease.
Renewal Submission Steps
- The renewal process happens in a certain order sequence.
- Examine the renewal notification or eligibility timeframe.
- Verify aircraft and owner details.
- Finish your renewal submission.
Tips on How to Renew Smoothly
- It is time. You can get corrections or clarifications made if you submit soon.
- Equally important is recordkeeping. Future compliance verification is supported by maintaining copies of renewals.
- The following lists highlight the most appropriate course of actions to take.
Top Strategies for Effective Renewal
- Examine registry details each year.
- Send renewal before expiration.
- Keep ownership information consistent.
- Store confirmations safely.
Importance of Long-Term Federal Aviation Administration Renewal
Renewal is essential for compliance with aviation over the long term. It allows for safety, accountability and continuity.
For plane owners, renewing protects operational rights. Regulators can be sure the registry is accurate. Reliable data improve oversight, communication, and enforcement outcomes.
From the perspective of the industry, regular renewals create confidence in the national registry system. It ensures transparency across ownership transfers and operational changes.
Though administrative, renewal indicates a wider commitment to aviation responsible. If handled as high priority, risk of regulations gets minimized and helps with the fleet management of aircraft.
Staying Compliant with Federal Aviation Administration
The process of renewal controlled by the Federal Aviation Administration is a linchpin of U.S. aviation compliance. It guarantees that aircraft registration documentation is effective and up-to-date.
By knowing renewal requirements, timelines and best practices, aircraft owners can avoid unnecessary disruption. National Aviation Center Successful renewal comes with preparation, accuracy, and timely submission. Delays miraculously happen because of human error. However, consistently managing the work process ensures we continue to meet deadlines.
In the end, regular renewing shows responsible aircraft ownership. It helps in safety oversight and legal clarity, and confidence in the aviation system over time.




